| Sorted by symbol | Sorted by Name | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sym | Name | Name | Sym |
| α | alpha radiation | acceleration | a |
| α | fine structure constant | alpha radiation | α |
| β | beta radiation | ampere | A |
| Δ | difference | angle | θ |
| ε | initial phase angle | angle of incidence | i |
| ε0 | permittivity of free space | angle of reflection | r |
| εr | relative permittivity | angle of refraction | r |
| η | efficiency | angular acceleration | a |
| η | viscosity | angular momentum | p |
| γ | gamma radiation | angular velocity | ω |
| γ | surface tension | area | A |
| ∫ | integral | atomic mass | A |
| λ | decay constant | atomic mass unit | u |
| λ | wavelength | atto | a |
| µ | coefficient of friction | Avogadros number | NA |
| µ | mass per unit length | beat frequency | fB |
| µ | micro | Becquerel | Bq |
µ | Thompson coefficient | beta radiation | β |
| µ' | coefficient of sliding friction | Bohr magneton | µB |
| µ0 | permeability of free space | Boltzmann constant | k |
| µB | Bohr magneton | candela | cd |
| µN | nuclear magneton | capacitance | C |
| µr | relative permeability | Celcius | C |
| ω | angular velocity | centi | c |
| ω | initial angular velocity | charge | Q |
| Ω | ohm | circumf. | C |
| Φ | magnetic flux constant | coefficient of friction | µ |
| π | pi | coefficient of sliding friction | µ' |
| Π | Peltier coefficient | conductance | G |
| ± | plus or minus | conductance quantum | G0 |
| Ψ | electric flux | conductivity | σ |
| ρ | resistivity | coulomb | C |
| σ | conductivity | critical angle | c |
| σ | Stefan Boltzmann constant | current | I |
| ∑ | sum | current density | J |
| θ | angle | deca | da |
| θ | temperature | decay constant | λ |
| a | acceleration | deci | d |
| A | ampere | depth | d |
| a | angular acceleration | difference | Δ |
| A | area | differential | 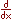 |
| a | atto | dioptre | D |
| A | nucleon number | displacement | s |
A | atomic mass | distance | s |
Ar | relative atomic mass | e | e |
| B | magnetic field strength | efficiency | η |
| Bq | Becquerel | electric field strength | E |
| Bs | magnetic field strength long solenoid | electric flux | Ψ |
| C | capacitance | electromotive force | E |
| C | Celcius | electron charge | e |
| c | centi | electronvolt | eV |
C | circumf/ | energy | E |
| C | coulomb | escape velocity | ve |
| c | critical angle | exa | E |
c | specific thermal capacity | exponential | e |
| c | speed of light | extension | e |
C | thermal capacity | Farad | F |
| cd | candela | Faraday constant | F |
| cmat | speed of light in material | femto | f |
Cp | parallel capacitance | final velocity | v |
Cs | series capacitance | fine structure constant | α |
| d | deci | focal length | f |
| d | depth | force | F |
| D | dioptre | frequency | f |
d | relative density | gamma radiation | γ |
| da | deca | gas constant | R |
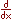 | differential | gas constant | R |
| e | e | giga | G |
| E | electric field strength | giga (computer 230) | G |
| E | electromotive force | gram | g |
| e | electron charge | gravitational acceleration | g |
E | energy | gray | Gy |
| E | exa | halflife | T½ |
| e | exponential | Hall coefficient | RH |
| e | extension | harmonic number | n |
E | Youngs modulus | Hartree Energy | EH |
| EH | Hartree Energy | hecto | h |
| eV | electronvolt | height | h |
| F | Farad | Henry | H |
| F | Faraday constant | Hertz | Hz |
| f | femto | horizontal measure | x |
f | focal length | hour | h |
| F | force | inductance | L |
| f | frequency | inductance | X |
| f | lens opening | initial angular velocity | ω |
| F' | sliding force | initial number of atoms | N0 |
| fB | beat frequency | initial phase angle | ε |
| G | conductance | initial velocity | u |
| G | giga | initial voltage | V0 |
G | giga (computer 230) | integral | ∫ |
| g | gram | Josephson constant | KJ |
| g | gravitational acceleration | Joule | J |
| G | universal gravitational constant | katal | kat |
| G0 | conductance quantum | Kelvin | K |
| Gy | gray | kilo | k |
| h | hecto | kilo (computer 210) | k |
| h | height | kilogram | kg |
| H | Henry | kinetic energy | KE |
| h | hour | length | l |
| h | Plancks constant | lens opening | f |
| Hz | Hertz | light year | ly |
| i | angle of incidence | Loschmidt constant | n0 |
| I | current | lumen | lm |
| I | moment of inertia | lux | lx |
| Io | maximum current | magnetic field strength | B |
| IRMS | RMS current | magnetic field strength long solenoid | Bs |
| J | current density | magnetic flux constant | Φ |
| J | Joule | mass | m |
| k | Boltzmann constant | mass of earth | mE |
| K | Kelvin | mass of electron | me |
| k | kilo | mass of neutron | mn |
| k | stiffness constant | mass of proton | mp |
k | kilo (computer 210) | mass per unit length | µ |
| kat | katal | maximum current | Io |
| KE | kinetic energy | maximum voltage | VMAX |
| KErot | rotational kinetic energy | mechanical advantage | MA |
| kg | kilogram | mega | M |
| KJ | Josephson constant | Mega (computer 220) | M |
| L | inductance | metre | m |
| l | length | micro | µ |
| L | original length | milli | m |
| l | specific latent thermal capacity | mole | mol |
| lm | lumen | moment of inertia | I |
| ls | string length | momentum | p |
| lx | lux | mutual inductance | M |
| ly | light year | myria | my |
| m | mass | nano | n |
| M | mutual inductance | neutron number | N |
| M | mega | Newton | N |
M | Mega (computer 220) | nuclear magneton | µN |
| m | metre | nucleon number | A |
| m | milli | number | n |
| MA | mechanical advantage | number of atoms | N |
| mE | mass of earth | number of moles | n |
| me | mass of electron | number of turns | N |
| mn | mass of neutron | ohm | Ω |
| mol | mole | original length | L |
| mp | mass of proton | parallel capacitance | Cp |
| mr | relative mass | parallel resistance | Rp |
| my | myria | Pascal | Pa |
| n | harmonic number | Peltier coefficient | Π |
| n | nano | period | T |
| N | neutron number | permeability of free space | µ0 |
| N | Newton | permittivity of free space | ε0 |
| n | number | peta | P |
N | number of atoms | peta (computer 215) | P |
n | number of moles | pi | π |
| N | number of turns | pico | p |
n | refractive index | Plancks constant | h |
N0 | initial number of atoms | plus or minus | ± |
| n0 | Loschmidt constant | potential energy | PE |
| NA | Avogadros number | power | P |
p | angular momentum | pressure | p |
| p | momentum | proton number | Z |
| P | peta | radian | rad |
P | peta (computer 215) | radius | r |
| p | pico | radius of curvature | r |
| P | power | radius of earth | rE |
| p | pressure | reactance | X |
| Pa | Pascal | reaction | R |
| PE | potential energy | refractive index | n |
| Q | charge | relative atomic mass | Ar |
| r | angle of reflection | relative density | d |
| r | angle of refraction | relative mass | mr |
| R | gas constant | relative permeability | µr |
| R | gas constant | relative permittivity | εr |
r | radius | resistance | R |
r | radius of curvature | resistivity | ρ |
R | reaction | RMS current | IRMS |
| R | resistance | RMS voltage | VRMS |
r | separation | rotational kinetic energy | KErot |
| r | source resistance | Rydberg constant | R∞ |
| R∞ | Rydberg constant | second | s |
| rad | radian | separation | r |
rE | radius of earth | series capacitance | Cs |
| RH | Hall coefficient | series resistance | Rs |
| RK | von Klitzing constant | Siemen | S |
| Rp | parallel resistance | Sievert | Sv |
| Rs | series resistance | sliding force | F' |
| s | displacement | source resistance | r |
| s | distance | specific latent thermal capacity | l |
| s | second | specific thermal capacity | c |
| S | Siemen | speed | s |
s | speed | speed of light | c |
| sr | steradian | speed of light in material | cmat |
| Sv | Sievert | Stefan Boltzmann constant | σ |
| T | period | steradian | sr |
T | temperature | stiffness constant | k |
| T | tension | string length | ls |
| T | tera | sum | ∑ |
T | tera (computer 212) | surface tension | γ |
| T | tesla | temperature | θ |
| t | time | temperature | T |
| t | tonne | tensile strain | Tst |
T | torque | tensile stress | Ts |
| T½ | halflife | tension | T |
| Ts | tensile stress | tera | T |
| Tst | tensile strain | tera (computer 212) | T |
| u | atomic mass unit | tesla | T |
| u | initial velocity | thermal capacity | C |
v | final velocity | Thompson coefficient | µ |
| V | vectra | time | t |
| v | velocity | tonne | t |
| v | vimto | torque | T |
| V | volt | universal gravitational constant | G |
| V | voltage | vectra | V |
| V | volume | velocity | v |
| V0 | initial voltage | velocity ratio | VR |
| ve | escape velocity | vertical measure | y |
| VMAX | maximum voltage | vimto | v |
| VR | velocity ratio | viscosity | η |
| VRMS | RMS voltage | volt | V |
| W | watt | voltage | V |
| W | weight | volume | V |
| W | work | von Klitzing constant | RK |
| Wb | Weber | watt | W |
| x | horizontal measure | wavelength | λ |
| X | inductance | Weber | Wb |
X | reactance | weight | W |
| X | xray | work | W |
| y | vertical measure | xray | X |
| y | yocto | yocto | y |
| Y | yotta | yotta | Y |
| Z | proton number | Youngs modulus | E |
| z | zepto | zepto | z |
| Z | zeta | zeta | Z |
www.DigitalDan.co.uk